
How to position a website for search engines
What is the positioning of a website
An effective website is a well-positioned one, in other words, a site visible among the search engine results. A good positioning (at least on the first page of the SERP) is relevant to attract a good number of users to your site and, possibly, to turn them into customers.
The positioning is the result of an optimization work on several fronts. We also remind you that the first places in the SERP are currently occupied by ads (web pages sponsored on Google Ads), an aspect that makes it practically impossible to get among the first places with organic traffic only.
Even if it cannot offer a guarantee of success (understood as conversions) a priori, the work to promote good positioning is essential for a website. Let’s try to list the good practices for the positioning of a website.
Text
– Content is king. Don’t be afraid to take the space you need to offer comprehensive content. Online brevity does not reward if it fails to offer added value to the reader. However, remember to format the text for the web, dividing it into titled paragraphs to facilitate reading.
– Frequently update your blog with original, comprehensive and consistent content with research intent.
– Try to develop a concept with the topic cluster method. A pillar page deals with the main topic exhaustively, but generally and links to in-depth pages related to the topic.
– Delete the pages that do not generate acceptable traffic volumes.
– Renew old pages with new titles and add a few update lines if needed.
Link building and sharing buttons
– Link related pages of your site to each other, especially if they contain keywords relevant to your business (internal links).
– Create outbound links (to pages of sites other than yours) and incoming links (acquire links from other sites, preferably authoritative). This leads to an increase in the domain authority.
– Be careful not to link to unavailable or unauthorized pages.
– Add social sharing buttons.
Photos and multimedia content
– Adopt a multimedia approach: videos and multimedia contents help keeping users on the page longer, significantly lowering the bounce rate (remember that a bounce rate that is too high is viewed quite negatively by the search engines).
– When uploading images, make sure that the format is supported (JPG, PNG, WEBP, SVG, GIF, BMP) and that the weight is not excessive; photos that are too heavy slow page loading and is a problem you want to avoid. Remember that 72 dpi is more than enough for the web. To give an order of magnitude, we try never to exceed the weight of 250/300 kb even for the largest photos.
– Name the images with the alt attribute, describing the content of the image in a few but exhaustive words. This is a practice that respects the accessibility requirements of the content for the visually impaired and helps Google’s algorithm to read and process the image.
User Experience
Today, the user experience counts much more than the keyword density. The quality and readability of the content are key factors. Therefore:
– Set the structure of the site in a clear and consistent way. Create a hierarchy that follows the natural flow of content (from the most general to the most specific).
– It helps the users to understand where they are and where they have to go to find what they’re looking for.
– Make navigation easier using breadcrumbs.
– Enter clear, simple and functional Call To Action.
Technical and monitoring aspects
– Enter the Analytics tracking code on the site and verify its ownership; subscribe to Google Webmasters Tool and connect the site (both are totally free).
– Through Search Console, send the sitemap to Google, which is the file that contains a list of all the pages of the site.
– Check loading speed via Page Speed Insights
– Enter the favicon (the icon that represents the brand and appears in the search engine tab for all pages of the site)
– Constantly monitor the performance of your site through Google Analytics (traffic, user behavior, data rates related to your target and much more …) and intervene if something does not perform as it should.
URL, meta title, meta description and keywords
The URL includes the domain name and other information to create a complete and unique web address, in order to address a browser to a specific page. As for the URL, we can give the following advice:
– When purchasing, make sure that the domain is available (not already used by someone else).
– Use the https: // protocol.
– If possible, already enter the most relevant keywords for your business in the URL. This involves a notable increase in the CTR.
The meta title is the title assigned to the page (in blue and purple, if the link has been clicked previously). The meta description is the short description of about 2 lines under the title. Meta tags are used to clarify the contents of the pages to the Google algorithms, explaining for which keywords you want to get ranking.
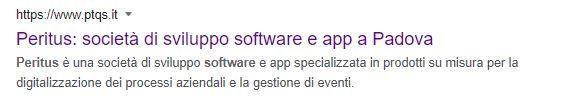
Also in this case:
– Enter strategic keywords in these fields to intercept traffic.
– Respect the character limits (about 60 for the meta title and 160 for the meta description). The CMS ususally provides a series of plugins that help managing this aspect, checking the number of characters and giving you feedback in terms of SEO effectiveness).
Remember that when one result gets more clicks than another, Google thinks it’s worthy of visits and places it higher in the SERP. Thus, curating your meta tags is essential.
What about your website?
If you need to renew your site, planning its contents from an SEO perspective, contact us without obligation! We will do what we can to help you.